It is already a good tradition at the end of the year to take a moment and wrap up the year, thus reminding myself of what was actually done, thus explaining to myself that maybe I am not as lazy as I think. However, in this post I would like to rather thank those colleagues who were with me in this. As such, let me very briefly summarize what happened (or rather with whom) and what to come in the first months of next year with the later to be spotlighted by me early next year accordingly.
This year I had the opportunity to share my experience, but more importantly, learn from others by participating in panels or plenary sessions, some of which stood out as generating some of the liveliest discussions during and after the events:
- “Citizen urban data and smart metropolis monitoring” together with Jaewon Peter Chun (President of World Smart Cities Forum), Redouane El Haloui (President of APEBI Fédération des technologies d’information de télécommunication et de l’offshoring), Mahdi Barouni (The World Bank), Khouloud Abejja (Digital Transformation Director, Agence de Développement du Digital-ADD), Youssef El Maddarsi (CEO Naoris Consulting) that held as part of a Casablanca Smart City event (read a bit more here);
- panel on Trust in AI together with Nicolas Cruz B., Korbinian Bösl, and Anamika Chatterjee as part of the Digital Life Norway conference oganized by Centre for Digital Life Norway (Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU)), with my big thanks to Elisabeth Hyldbakk, Ingrid Shields, Kam Sripada, and many more colleagues for hospitality;
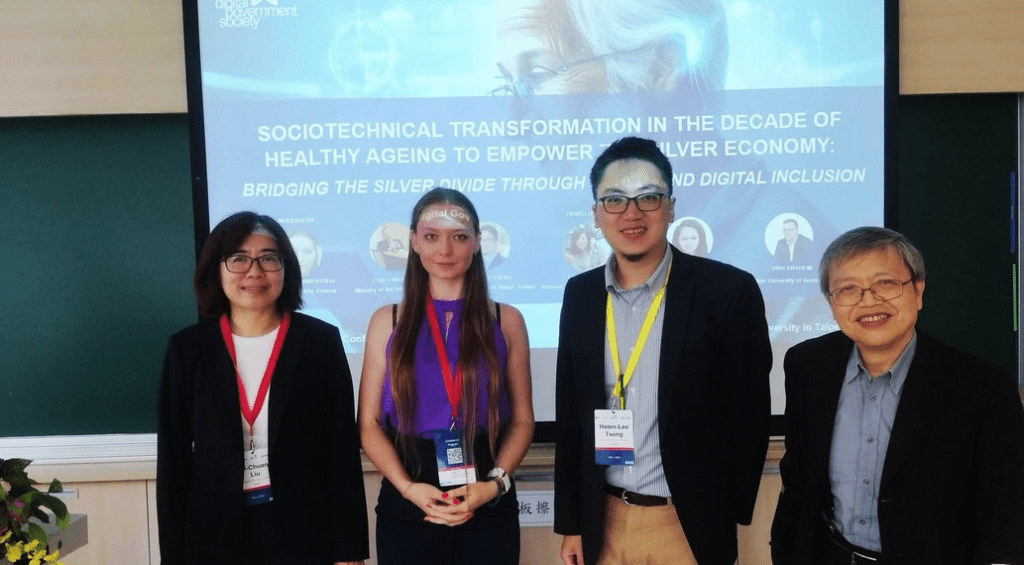
- “Sociotechnical Transformation in the Decade of Healthy Ageing to empower the Silver Economy: Bridging the Silver Divide through Social and Digital Inclusion” with Hsien-Lee Tseng, Chin-Chien Jao, Azmat Butt, Dirk Draheim, Li-chuan Liu as part of 25th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research (dg.o 2024) (read a bit more here)


To continue on discussions around research that I truly enjoyed, several conferences or tracks to which I served as one of organizers to be highlighted with credits to go to my colleagues, namely:
- EGOV2024 – IFIP EGOV-CeDEM-EPART 2024 “Emerging Issues and Innovations” Track with Marijn Janssen and Francesco Mureddu;
- Data for Policy 2024 “Digital & Data-Driven Transformation in Governance” track with Sarah Giest, Sharique Manazir, Keegan McBride, Francesco Mureddu, Sujit Sikder (a bit more here)
- 25th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research (dg.o 2024) “Sustainable Public and Open Data Ecosystems” with Anthony Simonofski, Anneke Zuiderwijk, Manuel Pedro Bolívar Rodriguez
Selected papers from DGO2024 and EGOV2024 were invited to the “Towards sustainable public and open data ecosystems” Special Section with Information Polity, which we successfully a few weeks ago with the very last preparations before we can announce its final version – big thanks to both co-editors – Anthony, Pedro, and Anneke, as well as Albert Meijer, Kim Willems, William Webster, who supported us in the process, and the authors – Mohsan Ali, Georgios Papageorgiou, Abdul Aziz, Euripidis Loukis, Yannis Charalabidis, Charalampos Alexopoulos, and Francisco Javier López Pellicer, Alejandra Vargas, Rikke Magnussen, Birger Larsen, and Ingrid Mulder and Hsien-Lee Tseng. Stay tuned for the information about this Section!
Together with Jérôme Chenal, Stéphane C. K. Tekouabou and El Arbi Allaoui Abdellaoui we almost finalized our “Emerging Data- and Policy-driven Approaches for African Cities Challenges” Special Issue with Cambridge Press Data & Policy journal – again, stay tuned!
While the two above are those we are ready with, there is another very special issue we have together with Asif Gill, Ina Sebastian, Martin Lněnička and Anushri Gupta and tremendous assistance of Katina Michael – Special Issue “Trustworthy Data Ecosystems for Digital Societies” with IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society (read a bit more here) and we look forward your submission by 30 June 2025 very much!
And of course, several conferences where I shared my own research, gathering feedback and inspiration for future research, with brightest moments coming from The 25th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research (DGO2024) (read a bit more here), and big thanks to my personal host Hsien-Lee Tseng, EGOV2024 and my special hosts Cesar Casiano Flores & Caterina Santoro, 27th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2024) (read a bit more here), International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS2024) (a bit more here), and several more, where I was fortunate this year to not only present my own research but also introduce my students to the community. Some of these conference papers have already expanded into journal papers, with some exciting news to share early next year!
I am also very grateful to my colleagues for their invitations to join the International Journal of Information Management (IJIM, Elsevier) and Government Information Quarterly (GIQ) Editorial Boards, Communication Committee at Digital Government Society (and one of its Chapter on which I will post later, similar to several other recent updates), and European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) FAIR Metrics and Digital Objects task force, which is rather continuation of the TF I participated in the past (“FAIR Metrics and Data Quality”).
On a slightly different note, similar to previous years, I continued delivering some courses and lectures to other universities, such as:
- “Crafting Success: The Art of Business Process Management” course for the International Week in Babeș-Bolyai University 🇷🇴, whose expanded version I also deliver to OVGU – Die Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg 🇩🇪;
- lecture for an Online International Training and Capacity Building Program-2024 (ITCBP) on “Data Management for AI in Cities”, organised by the School of Planning and Architecture, New Delhi 🇮🇳
- for the Federal University of Technology – Parana 🇧🇷 as part of Smart Cities course on the symbiotic relationship of Artificial Intelligence, Data Intelligence, Collaborative Intelligence, and Embodied Intelligence for urban planning and governance of Smart Cities;
- and several more events, including some local ones we organized for our current and prospective PhD students at the Institute of Tartu – hope to see all attendees with us!
I am also grateful for several recognitions I have received this year (e.g., being named the best reviewer for a journal, or called to be “the top 2% of scientists“ for the second year in a row (Stanford Elsevier Top Scientists List) and top 0.5% of all scholars worldwide (0.2% in Government specialty) by SholarGPS), but probably the proudest moment for every academic is the success of our students, and as such, I want to especially mention Kevin Kliimask, whose thesis recognized by the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Communications of Estonia at the annual Open Data Forum (Avaandmete foorum) as the best thesis of the year 🏆 🥇 🏅 (read a bit more here).














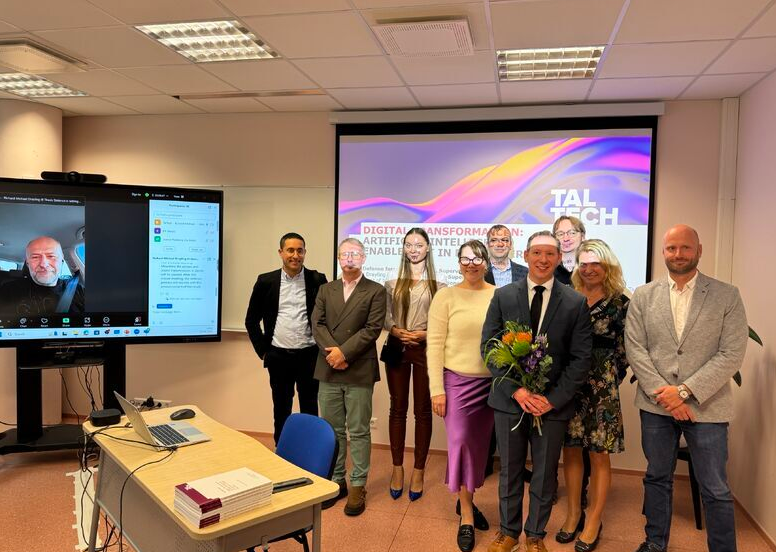
I also want to acknowledge achievements of others – this year I witnessed 3 PhD defenses and would like to congratulate Eric Jackson, Richard Dreiling and Lisa Miasayedava again, especially for such insightful discussions – I know I am quite a tough person to have in the committee (esp. as opponent – sorry Liza and Eric), but you all did a great job and I really enjoyed our discussions!



And I will skip the part about published conference and journal papers, as well as submitted project proposals and those currently in development. Instead, some disclaimer about what is to come, with some posting at later point:
- in the very first weeks of January, meet my very good colleagues– Anthony and Nicolas – at HICSS presenting our paper “Artificial Intelligence as a Catalyzer for Open Government Data Ecosystems: A Typological Theory Approach”, which has been already spotlighted several times, including by The Living Library, whose main goal is to identify the “signal in the noise”
- keep an eye open for several conferences for which together with colleagues of mine we organize (mini-) tracks, with probably the most important for me at the moment:
- AMCIS mini-track Sustainable Digital and Data Ecosystems – Navigating the Age of AI;
- DGO2025 – “Sustainable Public and Open Data Ecosystems for Inclusive and Innovative Digital Government” track we continue with Anthony Simonofski, Anneke Zuiderwijk;
- EGOV2025 – Emerging Issues and Innovations Track – we continue in the updated form welcoming Paula Rodriguez Muller who will be joining me and Francesco Murredu!
- And for Data for Policy CIC, we will slightly change the role we played the last year, and together with Sarah Giest, Bram Klievnik Iryna Susha, Florin Coman Kund, Leid Zejnilovic Laura, we are very excited to invite you to the Data for Policy CIC 2025 Conference (Leiden University, The Hague, Netherlands 🇳🇱) for which we serve as Regional Conference Committee
- Finally, do meet me at European Open Data Days 2025 in March to discuss recent (and future) advances in the world of open data with me sharing insights on how Artificial Intelligence can serve as a catalyst for transforming public and open data ecosystems, exploring the various AI roles at data, portal and ecosystem levels driving innovation, enhancing governance, and boosting citizen engagement;
- and meet me as a keynote for the International Conference on Innovative Approaches and Applications for Sustainable Development (I2ASD) in April with more details to come!



This is rather a very short list of the events and people I wanted to emphasize, and my apologizes if I missed someone (and I definitely missed). All in all, it was a busy and eventful year, – really grateful for all the opportunities it brought to me and lessons (both positive and negative, rather willing to have positive ones only though) and people I met. I really hope that the next year will be even better. And in this regard, I wish us all a peaceful, joyful and productive year!

Thank 2024 and bye! Welcome 2025! Happy 2025!