2025 is close to be over and looking back at 2025, what stays with me most is not the accumulation of roles, publications, or events, although each of them matters, but the sense that the work is gradually finding its place, creating space for better questions, and shaped, refined, sustained by people and conversations rather than metrics alone. This year marked a consolidation of my research agenda around digital, data, and AI governance, with a strong emphasis on responsible AI adoption, public value, and sustainable data ecosystems. It also continued earlier started transition – from building a research profile to more explicitly shaping research spaces, communities, and conversations.
From Research Agenda to Institutional Responsibility
In 2025, I was appointed Associate Professor of Applied AI and Information Systems, a role that formalized something that had already been happening in practice – working at the intersection of AI innovation, governance, and responsibility. This appointment aligned naturally with my work on responsible AI adoption in the public sector, research on data-centric challenges, governance models, and institutional readiness, and a growing focus on sustainable and trustworthy digital ecosystems, and as of this year on Green AI, including collaborative work with KNOW Center and ENFIELD.
At the University of Tartu, we also laid important foundations for the future – the establishment of the IDEAS Lab (Intelligent Distributed Environments and Systems), and hence my new role as lead of the Responsible Innovation and Digital Governance Team (RISING) – a space that, hopefully, will become more visible in 2026.
Research Milestones: Asking Better Questions About AI
A symbolic, but meaningful, milestone this year was publishing my 100th and 101st (IT people will get the point of the later number, too) scientific papers. These special papers are “Responsible AI Adoption in the Public Sector: A Data-Centric Taxonomy of AI Adoption Challenges” – the work that crystallizes our empirical research into a structured understanding of why responsible AI adoption remains difficult, even when technical solutions exist, and “Reflections on the nature of digital government research: Marking the 50th anniversary of Government Information Quarterly” marking the 50th anniversary of Government Information Quarterly – the top journal I read extensively as a master’s student, and now serve as an editorial board member, contributing reflections on the journal’s past, present, and future trajectory. That continuity — from reader to contributor to steward — feels particularly meaningful.
Beyond this, 2025 included some more contributions to Government Information Quarterly, Computer Law & Security Review, Telematics and Informatics, Information Polity, Data & Policy, EGOV2025, HICSS2025, CAiSE2025, DGO2025, and some more with topics ranging from data ecosystems, data and AI governance, post-bureaucratic governance, dark data, UX of open data portals to AI in education. What is more important, some of these papers were contributions of my students’ – from early master students to doctoral ones – my own or those more “adopted” ones I am always happy to collaborate with. All in all, seven students in total published their works this year and I hope for many more in the years to come!



Global Dialogue: From Keynotes to Fireside Chats
In 2025, I had the privilege to contribute to global conversations on AI and governance through keynotes, invited talks, panels, and workshops, including invited talk for EU Open Data Days 2025 on “Data for AI or AI for data,” panel on “AI and Data Science Revolutions” and “National Data Strategies in Europe” with Data for Policy, keynote “Responsible AI Adoption for a Sustainable Future: Balancing Opportunities and Risks“ for International Conference on Innovative Approaches and Applications for Sustainable Development, invited talk on “Mapping the Roadblocks: Towards Responsible Artificial Intelligence Adoption in the Public Sector“ for International Summer School on Digital Government and some more seminars and fireside chats with Cambridge University, LSE, The Governance Lab, Microsoft Open Data Policy Lab on future of open data in the age of (Gen)AI and AI governance among others. These conversations reaffirmed responsible data practices and even more so responsible AI is no longer a niche concern – it is now a core governance challenge across regions, policy domains, and institutional contexts.







Community Building: Workshops, Tracks, and Field-Shaping
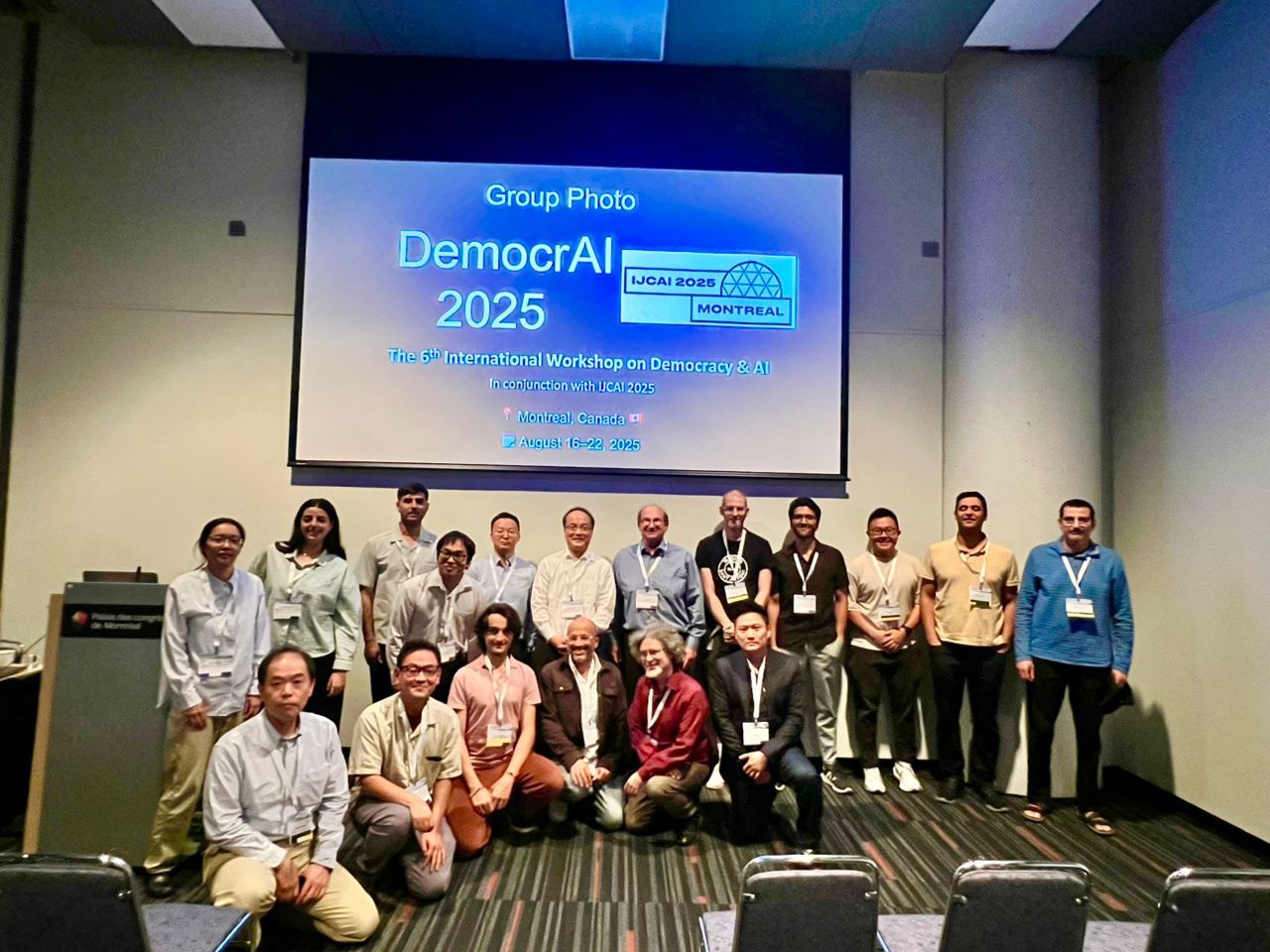
2025 was also a year of active field-building, through organizing and leading scholarly spaces where new ideas can emerge. Together with my colleagues we organized workshops at ECAI2025 (Green-aware AI), IJCAI2025, PRICAI2025 (AI and democracy and AI in public sector), CBI-EDOC2025 (Enterprise Architecture for Augmented Intelligence workshop) and (mini)tracks at HICSS2026 (Sustainable and Trustworthy Digital and Data Ecosystems for Societal Transformation), dg.o2025 (Sustainable Public and Open Data Ecosystems for Inclusive and Innovative Digital Government), EGOV2025 (Emerging Issues and Innovations). For the later one, we also organized Junior Faculty School and Doctoral Colloquium. Apart of this, I took several new editorial roles, including Senior Editor at IEEE TTS, as well as joined initiatives such as the AIS Women’s Network College (incl. as mentor), Women in AI, and Digital Statecraft Academy, which aims to guide fellows in navigating complex digital governance challenges and contribute to advancing responsible, inclusive, and sustainable policy and technology practices. I am very eager to see how these all will evolve looking forward contributing to the success of these joint efforts!
Perhaps one of the most surreal moments was hosting a Turing Award winner – a reminder of how far the field has come, and how much responsibility comes with shaping its future direction. Unfortunately, though, I missed meeting Yoshua Bengio in montreal this year, when my colleagues with whom we co-organized the workshop with IJCAI2025 made it, visiting his MILA lab… But one Turing award recipient at a time, I guess..










This year also brought external recognition, such as being ranked Top voice in Estonia in Data Science (as per Favikon), Top-1 researcher globally in Open Government and top Government and Engineering and CS researcher (as per ScholarGPS, according to last five years achievements), top 2% of scientists in Artificial Intelligence (as per Stanford University’s database). While I am grateful, among all achievements, the most rewarding was witnessing the success of my students and I hope much to come along both lines in the future. Their growth is a constant reminder that academic impact is not only measured in citations — but in confidence built, curiosity nurtured, and doors opened. At the end of the day, it is all about people. I am thus grateful to all the collaborators I am surrounded with – those I continue to learn from, and to those who now learn with me — both equally shape the work and sustain the motivation to carry it forward, as well as help to have some fun that is a special type of the fuel for our work!







Looking Ahead to 2026
The coming year will bring new responsibilities and, hopefully, opportunities. But above all, I hope 2026 continues what 2025 reinforced. As of now we already work hard on preparing several events to take place and I warmly invite you to consider joining us:
- HICSS2026 (Sustainable and trustworthy digital and data ecosystems for societal transformation), Hawaii, US, January 2026
- EGOV2026 (IFIP EGOV-CeDEM-EPART 2026) “Emerging Issues and Innovations” track, Greece, Athens, September 2026
- DGO2026 – 26th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research (dg.o) “Accountable and Inclusive Digital Ecosystems for Public Value Creation” track, June 2026
- AMCIS2026 –Human-AI Collaboration and Governance for Responsible and Sustainable Digital Ecosystems, Nevada, US, August 2026
- DGO2026 – 26th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research (dg.o) “Emerging topics” track , Omaha, US, June 2026
- DB&IS2026 – The 17th International Baltic Conference on Digital Business and Intelligent Systems (DB&IS), Tartu, Estonia, June 2026




If you’d like to continue these conversations in person, you can also find me speaking at events such as ICDEc2026, ISIoT2026, and AI Summit Europe 2026, discussing questions like What happens when AI ambitions collide with governance capacity, legitimacy, and readiness? How do we design AI-enabled systems that don’t collapse under institutional and societal pressure? Are we moving from e-government to AI_government or maybe even toward something closer to an agentic state — and what does that really mean? If you work on AI, data, governance, sustainability, or public value, I would love to meet you — to exchange ideas, challenge assumptions, and think together about how to design systems that are not only intelligent, but also legitimate, resilient, and trustworthy.
Wishing a peaceful and joyful holiday season, and a thoughtful, kind, and inspiring year ahead to all of us!