Today (May 16, 2023), I had a pleasure to deliver one more guest lecture for master and doctoral students of the Federal University of Technology – Paraná (Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná (UTFPR)) as part of Smart Cities course delivered by prof. Regina Negri Pagani. This time the topic of my lecture was “Open Data Ecosystems in and for sustainable development of data-driven smart cities and Society 5.0”.
As part of this lecture we talked about open data and open government data (OGD) phenomena and how they evolved over years, what the open data ecosystem is and what constitutes it. I then tried to put it in the context of Brazil reflecting on the current state-of-the-art of open government and OGD in Brazil and its cities referring to both Open Government Partnership (Brazil was one of the the founding countries of OGP), existing OGD, transparency and central bank portals, studies that explored effects of predictors of citizens’ attitudes and intention to use OGD (*by de Souza, Ariel Antônio Conceição, Marcia Juliana d’Angelo, and Raimundo Nonato Lima Filho), factors influencing civil servant’s intention to disclose data (**by Fernando Kleiman, Sylvia J.T. Jansen, Sebastiaan Meijer, Marijn Janssen), as well as the relationship between transparency and open data initiatives in five Brazilian cities (identifying that they are not related for these five cities) (***by Araújo, Ana Carolina, Lucas Reis, and Rafael Cardoso Sampaio)



Then, presenting the concepts of Smart Cities and their “generations”, Sustainable Cities and Sustainable Smart Cities, as well as Society 5.0 (aka Super Smart Society and Society of imagination), I highlighted the overlaps and interweavings of the above and how the development of one contributes to the other, i.e. how interrelated they are and how complex this large ecosystem is.
And then, the remaining part of the lecture was focused around the topic of open data ecosystems starting with the current state of the art around the topic, i.e. different and similar definitions, components, characteristics etc., and finally the study we conducted some time ago with my colleagues from Czech Republic, Poland, Finland, Germany and Latvia, namely “Transparency of open data ecosystems in smart cities: Definition and assessment of the maturity of transparency in 22 smart cities“**** published in . Sustainable Cities and Society (Elsevier), in which we:
- developed a benchmarking framework to assess the level of transparency of open data ecosystems in smart cities consisting of 36 features by adapting transparency-by-design framework for open data portals (*****by Lněnička and Nikiforova, 2021);
- investigated smart city data portals’ compliance with the transparency requirements, where the developed framework has been applied to 34 portals representing 22 smart cities, allowing determination of the level of transparency maturity at general, individual, and group levels;
- developed four-level transparency maturity model to allow the classification of the portal as developing, defined, managed, and integrated, thereby allowing to identify key issues to be transformed into corrective actions to be included into agenda and navigate to the set of more competitive portals;
- ranked the portals concerned based on their transparency maturity, thereby allowing more successful portals to be identified in order to be used as an example for improving overall or feature-wised performance by providing recommendations for the identification and improvement of current maturity level and specific features;
- conceptualized an open data ecosystem in the context of a smart city (!!!) and determined its key components considering the data-centric and data-driven infrastructure and other components and relationships, using the system theory approach;
- on the basis of the dominant components of data infrastructure, defined five types of current open data ecosystems (see below) thereby opening up a new horizon for research in the area of sustainable and socially resilient smart cities by means of open data and citizen-centered open smart city governance.
Our definition of open data ecosystem in the smart city context , established based on the knowledge and experience of the experts involved and observations made during the study is:
“systematic efforts to integrate ICT and technologies into city life to deliver citizen-centric, better-quality services, solutions to city problems with open data published through the data-centric and data-driven infrastructure.”


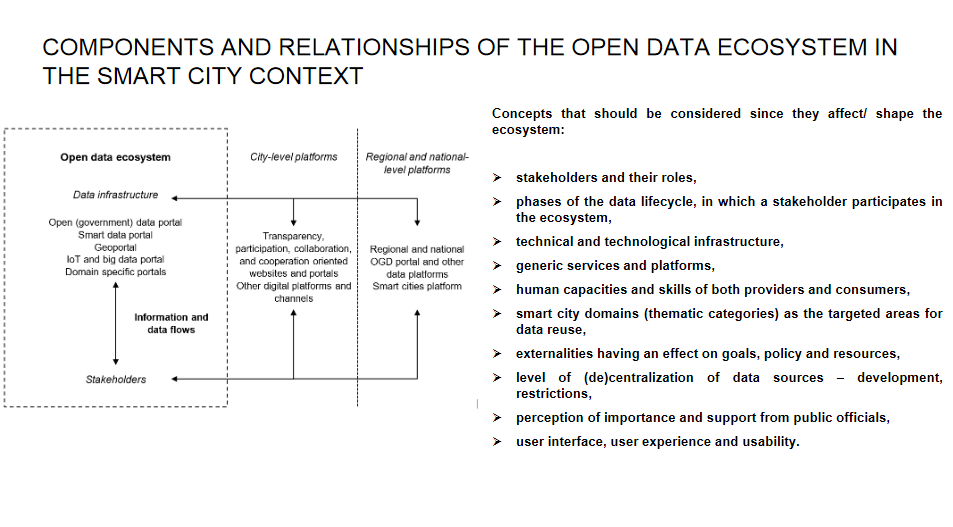
However, the concepts that affect/shape the ecosystem are:
- stakeholders and their roles,
- phases of the data lifecycle, in which a stakeholder participates in the ecosystem,
- technical and technological infrastructure,
- generic services and platforms,
- human capacities and skills of both providers and consumers,
- smart city domains (thematic categories) as the targeted areas for data reuse,
- externalities affecting goals, policy, and resources,
- level of (de)centralization of data sources – development, restrictions,
- perception of importance and support from public officials,
- user interface, user experience, and usability.
As for the types of current open data ecosystems, we identified 5 types that are as follows:
- type#1: the city’s OGD portal is the center of the data infrastructure, and all OGD, including those labeled as smart, are published and centralized through it. For this type of open data ecosystem, other websites that had previously provided open data or other services to access public sector information have been replaced by the OGD portal. The focus is on datasets, providing features to work with them, reuse them, and make all data requests transparent in one place;
- type#2: this ecosystem also usually has the OGD portal as the central point, but other portals and platforms publish open data. The smart data portal and online city dashboards focusing on different dimensions such as transport, health, air quality, etc., are important components of this ecosystem;
- type#3: a decentralized type of ecosystem that includes many components such as OGD portal, smart data portal, geodata portal, etc. However, it increases the ecosystem’s complexity, which is more difficult to manage and less usable for stakeholders
- type#4: the smart city portal focused on projects and services is usually the center of this ecosystem, but it is not the priority to provide data and appropriate features to reuse them. Most services are developed by public sector organizations, research institutions, or businesses and provided to citizens;
- type#5: apart from the city’s OGD portal, there are additional transparency-, participation-, collaboration-, and cooperation-oriented websites and portals to support the formation and improvement of relations between stakeholders. This type of ecosystem is focused on processes to improve open data reuse.
Sounds interesting? Read the article here and see other recommended articles below! 🙂
This was then wrapped up by emphasizing key overseen topics that are paid to little attention to, although being crucial for a sustainable public data ecosystem.
And I can only hope that this lecture was just a little bit as interesting as my dear colleague prof. Regina Negri Pagani characterized it! It is always pleasure to hear her feedback, as her comments are so gentle and inspiring! And there is nothing better than hear such wonderful and positive feedback and an immediate invitation for the next editions of this course, which will be my pleasure – this was the 2nd edition of the course, when I served as a guest lecture and will be definitely glad to make this yet another good tradition!
References:
*de Souza, Ariel Antônio Conceição, Marcia Juliana d’Angelo, and Raimundo Nonato Lima Filho. “Effects of Predictors of Citizens’ Attitudes and Intention to Use Open Government Data and Government 2.0.” Government Information Quarterly 39.2 (2022): 101663.
**Kleiman, F., Jansen, S. J., Meijer, S., & Janssen, M. (2023). Understanding civil servants’ intentions to open data: factors influencing behavior to disclose data. Information Technology & People.
***Araújo, Ana Carolina, Lucas Reis, and Rafael Cardoso Sampaio. “Do transparency and open data walk together? An analysis of initiatives in five Brazilian capitals.” Media Studies 7.14 (2016).
****Lnenicka, M., Nikiforova, A., Luterek, M., Azeroual, O., Ukpabi, D., Valtenbergs, V., & Machova, R. (2022). Transparency of open data ecosystems in smart cities: Definition and assessment of the maturity of transparency in 22 smart cities. Sustainable Cities and Society, 82, 103906.
*****Lnenicka, M., & Nikiforova, A. (2021). Transparency-by-design: What is the role of open data portals?. Telematics and Informatics, 61, 101605.
Some other studies you might be interested:
- Nikiforova, A., Alor, M. A., & Lytras, M. D. (2022). The role of open data in transforming the society to Society 5.0: a resource or a tool for SDG-compliant Smart Living?. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.11784.
- Nikiforova, A. (2021). Smarter open government data for society 5.0: are your open data smart enough?. Sensors, 21(15), 5204.
- Nikiforova, A. (2023). Open Data Hackathon as a Tool for Increased Engagement of Generation Z: To Hack or Not to Hack?. In Electronic Governance with Emerging Technologies. EGETC 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, Springer, Cham.
- McBride, K., Nikiforova, A., and Lnenicka, M. (2023) ‘The Role of Open Government Data and Co-Creation in Crisis Management: Initial Conceptual Propositions from the COVID-19 Pandemic’, Information Polity, vol. Pre-press, 10.3233/IP-220057
- Nikiforova A., Zuiderwijk A. (2022) Barriers to openly sharing government data: towards an open data-adapted innovation resistance theory, In 15th International Conference on Theory and Practice of Electronic Governance (ICEGOV 2022). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 215–220
- Tékouabou, S. C., Chenal, J., Azmi, R., Toulni, H., Diop, E. B., & Nikiforova, A. (2022). Identifying and Classifying Urban Data Sources for Machine Learning-Based Sustainable Urban Planning and Decision Support Systems Development. Data, 7(12), 170.
- Nikiforova, A. (2020, October). Timeliness of open data in open government data portals through pandemic-related data: a long data way from the publisher to the user. In 2020 Fourth International Conference on Multimedia Computing, Networking and Applications (MCNA) (pp. 131-138). IEEE.
- Nikiforova, A., & Lnenicka, M. (2021). A multi-perspective knowledge-driven approach for analysis of the demand side of the Open Government Data portal. Government Information Quarterly, 38(4), 101622
- Nikiforova, A., & McBride, K. (2021). Open government data portal usability: A user-centred usability analysis of 41 open government data portals. Telematics and Informatics, 58, 101539
- Lněnička, M., Nikiforova, A., Saxena, S., & Singh, P. (2022). Investigation into the adoption of open government data among students: The behavioural intention-based comparative analysis of three countries. Aslib Journal of Information Management.
- Nikiforova A. (2021) Towards enrichment of the open government data: a stakeholder-centered determination of high-value data sets for Latvia: Stakeholder-centered determination of High-Value Open Government Data sets, 14th International Conference on Theory and Practice of Electronic Governance Proceedings, (ICEGOV 2021), October 6-8, 2021, Athens, Greece, ACM, New York, NY, USA
- Nikiforova, A. (2020). Comparative analysis of national open data portals or whether your portal is ready to bring benefits from open data. In IADIS International Conference on ICT, Society and Human Beings (pp. 21-23)
- Nikiforova, A. (2020). Assessment of the usability of Latvia’s open data portal or how close are we to gaining benefits from open data. In IADIS 14th International Conference on Interfaces and Human Computer Interaction (pp. 51-28)
- Nikiforova, A. (2020). Definition and Evaluation of Data Quality: User-Oriented Data Object-Driven Approach to Data Quality Assessment. Baltic Journal of Modern Computing, 8(3), 391-432