It finally took place! EGOV2023 – IFIP EGOV-CeDEM-EPART – one of the most recognized conference in e-Government, ICT and public administration and related topics (incl., Smart Cities, Sustainability, Innovation and many more) that lasted 3 days in charming city of Budapest (Hungary) is over, and I am here to reflect on it (just in a few words), since although these were just 3 days, they were very busy and full of insights, as well as activities, since every day I took another role, i.e., day#1 – presenter of the paper, day#2 – workshop organizer, day#3 – chair of two out of three sessions of “Emerging Issues and Innovations” track I co-chaired together with Marijn Janssen, Csaba Csaki and Francesco Mureddu. Not to forget, in this conference I am also a program committee of Open Data track.
Let me now provide a few insights on all these days, including my roles.
Let’s start with day#1… After conference opening by Ida Lindgren and Csaba Csaki – our local host, who did a great job – organized a very unique conference with exceptionally rich social programme, a brilliant keynote talk was delivered by Professor Yogesh K Dwivedi (possibly the most impactful researcher in the area) on Metaverse for Government and associated Challenges, Opportunities, as well as Future Research Agenda, as part of which the claim of a lack of studies on this topic was made. Luckily, our track “Emerging Issues and Innovations” has accepted one paper on Metaverse in digital government, which was the only at the conference, however, unfortunately, the discussion had not happened due to earlier departure of Yogesh and late arrival of authors. Anyway, almost immediately after the keynote the session, where I delivered a talk on HVD determination “Towards High-Value Datasets determination for data-driven development: a systematic literature review” (authors: Nikiforova, Rizun, Ciesielska, Alexopoulos, Miletić) took place. Just to remind you, I posted on this paper before – this is that paper, which has been already named “signal in the noise“, in which we asked ourselves and the current body of the knowledge (this is a systematic literature review-driven study):
❓how is the value of the open government data perceived / defined? Are local efforts being made at the country levels to identify dataset that provide the most value to stakeholders of the local open data ecosystem?
❓What datasets are considered to be of higher value in terms of data nature, data type, data format, data dynamism?
❓What indicators are used to determine HVD?
❓Whether there is a framework for determining country-specific HVD? I.e., is it possible to determine what datasets are of value and interest for their reuse & value creation, taking into account the specificities of the country, e.g., culture, geography, ethnicity, likelihood of crises and/or catastrophes.
Although neither OGD, nor the importance of data value are new topics, scholarly publications dedicated to HVD are very limited that makes study unique and constituting a call for action – probably this is also why it it is recommended for reading not only by us but also by The Living Library (by New York University, NYU Tandon School of Engineering, govlab). All in all, we have established some knowledge based, incl. several definitions of HVD, data-related aspects, stakeholders, some indicators and approaches that can now be used as a basis for establishing a discussion of what a framework for determining HVD should look like, which, along with the input we received from a series of international workshops as part of ICEGOV2022, ICOD2022 and DGO2023 with open data experts could enrich the common understanding of the goal, thereby contributing to the next open data wave.
👉Read the paper here
👉See slides here
👉Find supplementary data in open access at Zenodo here
Here I am very grateful to session attendees for raising a discussion around the topic, where some of those comments confirmed once more the correctness of both the problem statement and our future plans – thanks a lot!
Day#2 of started with another keynote talk, whcih this time delivered by Andras Koltay (President of the National Media and Infocommunications Authority and the Media Council of Hungary) on the protection of freedom of expression from social media platforms – very different but yet very insightful talk. Then, my second role of the workshop organizer and chair followed. As part of our workshop “PPPS’2023 – Proactive and Personalised Public Services: Searching for Meaningful Human Control in Algorithmic Government” (chairs: Anastasija Nikiforova, Nitesh Bharosa, Dirk Draheim, Kuldar Taveter). As part of this workshop, which took place in a hybrid mode (not an easy task), we initiated a discussion about personalised and Proactive Public Services, i.e.:
🎯talked about the concepts of public services, reactive and proactive models of public services, and models of their personalization;
🎯asked participants to share their views on public services and the levels of proactivity and personalisation of these services in their countries aiming to develop concepts for holistic proactive and personalised public service delivery;
🎯tried to establish a clearer vision of the “as-is” model and the necessary transition to the “to-be” model, their underlying factors, as well as pitfalls of which governments should be aware when designing, developing, and setting up proactive and personalised public services, trying to understand what are those emerging technologies that will likely have greater effect on public services in terms of both driving them or creating obstacles / barriers for their development and maintenance.
Read a bit more 👉 here
Special thanks to all participants, who attended and were very active (and survived)!
And now a few insights from day#3, when three sessions of our Emerging Issues and Innovations track (chairs: Marijn Janssen, Anastasija Nikiforova, Dr. Csaba Csaki, Francesco Mureddu) finally took place, where I was delighted to chair two of these sessions. Within these three sessions, 8 very diverse, but at the same time super interesting and insightful talks were delivered (predominantly from the United Nations University and Sweden), namely:
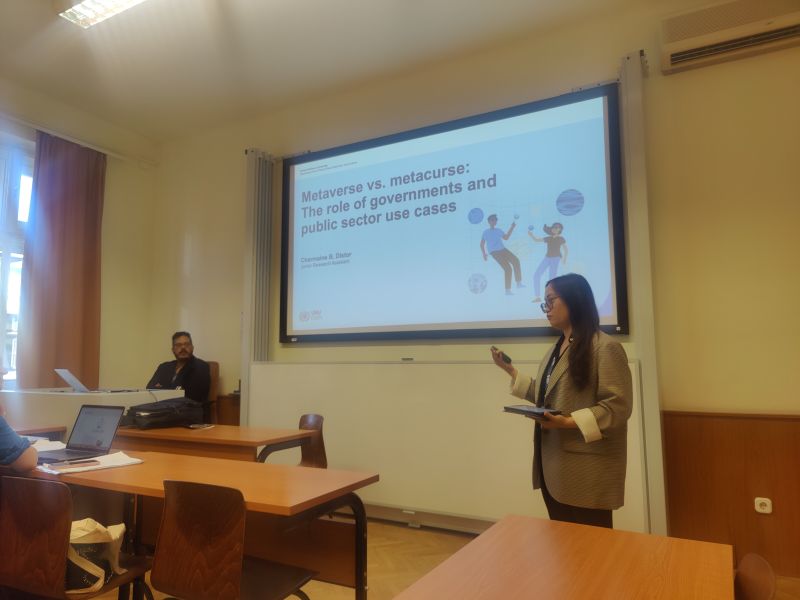
✍Metaverse vs. metacurse: The role of governments and public sector use cases by Charmaine Distor, Soumaya Ben Dhaou, & Morten Meyerhoff Nielsen that can be seen as a continuation of the keynote talk by Prof. Yogesh Dwivedi delivered at the 1st day;
✍Dynamic Capabilities and Digital Transformation in Public sector: Evidence from Brazilian case study by Larissa Magalhães;
✍Affording and constraining digital transformation: The enactment of structural change in three Swedish government agencies by Malin Tinjan, Robert Åhlén, Susanna Hammelev Jörgensen & Johan Magnusson
✍The Vicious Cycle of Magical Thinking: How IT Governance Counteracts Digital Transformation by Susanna H. Jörgensen, Tomas Lindroth, Johan Magnusson, Malin Tinjan, Jacob Torell & Robert Åhlen
✍Buridan’s Ass: Encapsulation as a Possible Solution to the Prioritization Dilemma of Digital Transformation by Johan Magnusson, Per Persson, Jacob Torell & Ingo Paas
✍Measuring digital transformation at the local level: assessing the current state of Flemish municipalities by Lieselot Danneels & Sarah Van Impe
✍Blockchain and the GDPR – the shift needed to move forward by Inês Campos Ruas, Soumaya Ben Dhaou & Zoran Jordanoski
✍Construct Hunting in GovTech Research: An Exploratory Data Analysis by Mattias Svahn, Aron Larsson, Eloisa Macedo and Jorge Bandeira
Read papers 👉 here, here & here
Big thanks go to both authors and presenters, as well as the audience, who was very active (even despite the fact that it was the very last day of the conference) and made these sessions a success!
And right after these two sessions, the third keynote by Laszlo Trautmann “The ethics of expertise – the political economy implications of AI”.
And the last but not the least, yet another social event – wine tasting at Etyeki Kúria Borászat / Winery, which was the perfect happy end of the EGOV2023!
Exceptional organization by Corvinus University of Budapest, Csaba Csaki and his team, International Federation for Information Processing (IFIP), Digital Government Society – cheers!🍷🍷🍷