Considering that in last weeks I was pretty active in delivering very many talks, let me use this post to summarize some of them thereby remaining them in my memory as well as allowing you, my dear reader, to pick up some ideas or navigate to some projects (both projects, initiatives, postgraduate programs, joint workshops or “lunchs” for business and academia) of your interest. So this post is less about self-advertisement and my role in the below discussed events as both panelist, keynote, guest lecturer, invited speaker and expert, but more about very interesting projects, initiatives and labs currently running in different countries and at different scales – local, national, regional and international. And as “thank you” for the organizers of each of them, I would like to shed a light on them in this post, drawing your attention to them!
All in all, this post is about participating as a panelist for One Conference 2022, keynote for African Smart Cities Lab projects’ workshop (Morocco, Ghana, Tunisia, South Africa, Rwanda, Benin, Switzerland), Guest Lecture for master and doctoral students of the Federal University of Technology – Paraná (UTFPR, Postgraduate Program in Production Engineering, Brasil), and invited speaker / expert for monthly “Virtual Brown Bag Lunch” (Mexico), and EFSA & EBTC joint project (Italy) on the creation of a standard for data exchange in support of automation of Systematic Review.
So, let’s start with the most spontaneous, namely “Integration of open data and artificial intelligence in the development of smart cities in Africa” workshop organized as part of the African Cities Lab Project, where I was invited as a keynote speaker. Actually, African Smart Cities Lab project is a very interesting initiative I recently was glad to get familiar with. It is a joint initiative led by École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (Switzerland), the Kwame Nkrumah’ University of Science and Technology, Kumasi (Ghana), the UM6P – Mohammed VI Polytechnic University (Maroc), Sèmè City campus (Benin), the Faculty of Sciences of Bizerta – University of Carthage (Tunisia), the University of Cape Town (South Africa), and the University of Rwanda that aims to create a digital education platform on urban development in Africa, offering quality MOOC and online, continuing education training for professionals. It is also expected to act as a forum for the exchange of digital educational resources and the management and governance of African cities to foster sustainable urban development. The very first workshop took place July 5 in an online mode, where 9 speakers were invited to share their experience on this topic and allow setting the scene for the development of African Smart Cities, considering their potential, but also some bottlenecks.




All in all, two very fruitful sessions with presentations delivered by me, Vitor Pessoa Colombo, Constant Cap, Oualid Ali, Jérôme Chenal, Nesrine Chehata, AKDIM Tariq, Christelle Gracia Gbado, Willy Franck Sob took place and raised a lot of questions, finding the answers for many of them. My talk was titled “Open data and crowdsourced data as enablers and drivers for smart African cities” (see slides below…)
Here, let me immediately mention another activity – a Guest Lecture “The role of open data in the development of sustainable smart cities and smart society“, I delivered to students of the Federal University of Technology – Parana (UTFPR, Brazil) and, more precisely so-called PPGEP program – Postgraduate Program in Production Engineering (port. Programa de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia de Produção), in scope of which I was pleasured to raise a discussion on three topics of particular interest – open data, Smart City, and Society 5.0, which are actually very interrelated. This also allowed me to refer to one of our recent studies – Transparency of open data ecosystems in smart cities: definition and assessment of the maturity of transparency in 22 smart cities – published together with my colleagues – Martin Lnenicka, Mariusz Luterek, Otmane Azeroual, Dandison Ukpabi, Visvadis Valtenbergs, and Renata Machova in Sustainable Cities and Society (Q1, Impact Factor: 7.587, SNIP: 2.347, CiteScore: 10.7).
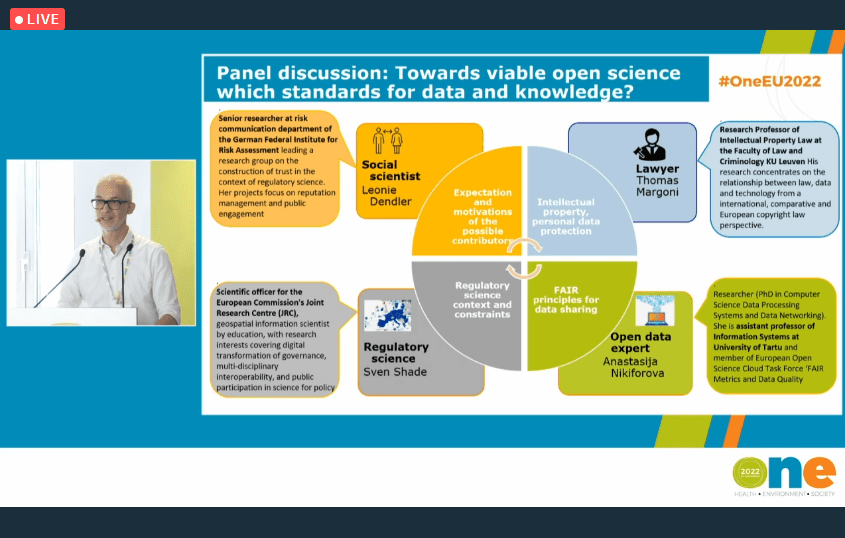
And now, it’s time to turn to two events organized by European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The first and probably the most “crowded” due to a very high rate of the attendance was the ONE Conference 2022 (Health, Environment, Society), which took place between June 21 and 24, Brussels, Belgium. It was co-organised by European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and its European sister agencies European Environment Agency, European Medicines Agency, European Chemicals Agency, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), but if you are an active follower of my blog, you know this already, same as probably remember that I posted about this event previously inviting you to join us in Belgium or online. Since I have elaborated on the course of the event, its main objectives and tracks, I will not repeat this information. Instead, let me briefly summarize key takeaways with a particular focus on the panel for which I served as a panelist – the “ONE society” thematic track, panel discussion “Turning open science into practice: causality as a showcase”. It was a very nice experience and opportunity for sharing our experience on obstacles, benefits and the feasibility of adopting open science approaches, and elaborate on the following questions (although they were more but these one are my favorites):
💡Can the use of open science increase trust to regulatory science? Or does it increase the risk to lose focus, introduce conflicting interests and, thus, threaten reputation? What are the barriers to make open science viable in support to the scientific assessment process carried out by public organizations?
💡What are the tools/ methods available enabling, supporting and sustaining long term open science initiatives today and what could be envisaged for the future?
💡Do we need a governance to handle open data in support to scientific assessment processes carried out by regulatory science bodies?
💡How the data coming from different sources can be harmonized making it appropriate for further use and combination?
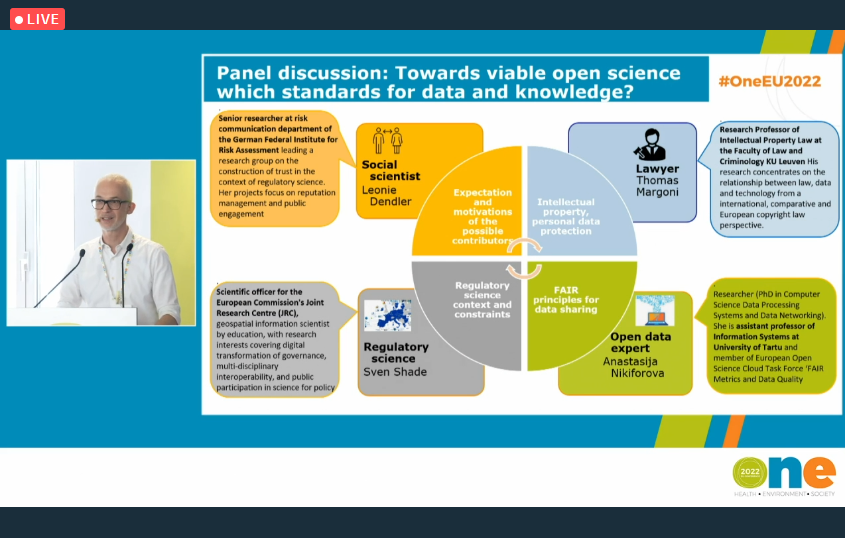



These and many more questions were discussed by panelists with different background and expertise, which were nicely presented by European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) breaking down our experience in four categories – social science (Leonie Dendler, German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment BfR), open data expert (Anastasija Nikiforova,) EOSC Association, University of Tartu, Institute of Computer Science, lawyer (Thomas Margoni, KU Leuven ), regulatory science (Sven Schade, Joint Research Centre, EU Science, Research and Innovation). Many thanks Laura Martino, Federica Barrucci, Claudia Cascio, Laura Ciccolallo, Marios Georgiadis, Giovanni Iacono, Yannick Spill (European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)), and of course to Tony Smith and Jean-François Dechamp (European Commission). For more information, refer to this page.
And as a follow-up for this event, I was kindly invited by EFSA to contribute to setting the scene on the concept of ‘standards for data exchange’, ‘standards for data content’ and ‘standards for data generation’ as part of European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and Evidence-Based Toxicology Collaboration (EBTC) ongoing project on the creation of a standard for data exchange in support of automation of Systematic Review (as the answer to the call made in “Roadmap for actions on artificial intelligence for evidence management in risk assessment”). It was really nice to know that what we are doing in EOSC Association (Task Force “FAIR metrics and data quality”) is of interest for our colleagues from EFSA and EBTC.
Also, it was super nice to listen other points of view and get involved in the discussion with other speakers and organisers – Elisa Aiassa, Angelo Cafaro, Fulvio Barizzone, Ermanno Cavalli, Marios Georgiadis, Irene Pilar, Irene Muñoz Guajardo, Federica Barrucci, Daniela Tomcikova, Carsten Behring, Irene Da Costa, Raquel Costa, Maeve Cushen, Laura Martino, Yannick Spill, Davide Arcella, Valeria Ercolano, Vittoria Flamini, Kim Wever, Gunn Vist, Annette Bitsch, Daniele Wikoff, Carlijn Hooijmans, Sebastian Hoffmann, Seneca Fitch, Paul Whaley, Katya Tsaioun, Alexandra Bannach-Brown, Ashley Elizabeth Muller, Anne Thessen, Julie McMurray, Brian Alper, Khalid Shahin, Bryn Rhodes, Kaitlyn Hair. The next workshop is expected to take place in September with the first draft ready by the end of this year and presented during one of the upcoming events. More info on this will follow 🙂
In addition, I was asked by my Mexican colleagues to deliver an invited talk for monthly “Virtual Brown Bag Lunch Talks” intended for the Information Technologies, Manufacturing, and Engineering Employees in Companies associated with Index Manufacturing Association (Mexico, web-based). After discussing several topics with the organizers of this event, we decided that this time the most relevant talk for the audience would be “Data Security as a top priority or what Internet of Things (IoT) Search engines know about you“. Again, if you are an active follower, you will probably realize quickly that it is based on a list of my previous studies – study#1, study#2, study#3 and book chapter.


All in all, while these were just a few activities I was busy with during the last weeks and, these weeks were indeed very busy but extreeeemely interesting with so many different events! I am grateful to all those people, who invited me to take part in them and believe that this is just one of the opportunities we had to collaborate and there are many more in the future!