In response to several requests, I finally completed the very first blog post on data quality management. In this post, I’ve mainly “set the scene” with the intention of publishing several more in-depth blog posts related to specific areas of my interest within data quality management, including but not limited to AI-augmented data quality management.
As for now, this post is focused primarily on my personal opinion (experience-based) what influences the choice of the data quality management approach (i.e., smth very similar to what I talked about at HackCodeX Forum I posted about earlier, and where the photo comes from).
Tag data analytics
The United Nations University EGOV’s repository platform and five of my articles it recommends 📖📚🧐
Recently, the United Nations University announced the launch of the United Nations University EGOV’s repository platform – a centralized hub of specialized repositories tackling global challenges, which is dedicated to two topics – EGOV for Emergencies that provides a set of content on innovations in digital governance for emergency response, and Data for EGOV is the repository intended “to supports policymakers, decision-makers, researchers, and the community interested in digitally transforming the public sector through emerging technologies and data. The repository combines diverse academic documents, use cases, rankings, best practices, standards, benchmarking, portals, datasets, and pilot projects to support open data, quality and purpose of open data, application of data techniques analytics in the public sector, and making cities smarter. This repository results from the “INOV.EGOV-Digital Governance Innovation for Inclusive, Resilient and Sustainable Societies” project on the role of open data and data science technologies in the digital transformation of State and Public Administration institutions“. The latter, recommends 286 reading materials (reports, articles, standards etc.) I find to be very relevant for the above described, and highly recommend to surf through. However, what made me specially happy while browsing this collection, is the fact that five of these reading materials are articles (co-)authored by me. Therefore, considering that not always I keep track of what I conducted in past, let me use this opportunity to reflect on those studies, in case you had not came across them previously, as well as to refresh mine memories (some of them dated back to times, when I worked on my PhD thesis).

By the way, every article is accompanied with tags that enrich keywords by which that article was described by authors, with a particular attention being paid to main topics, incl. “data analytics”, “smart city”, “open data”, “sustainability” etc., where for “the latter”sustainability”, tagging based on the compliance with a specific Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) takes place, thereby allowing to filter out relevant articles by a specific SDG or find out what SDG does your article contributes, where although while conducting research I kept in mind some of those I find my research more suited with, for one of them (the last one in the list) I was pretty surprised to see that it is very SDGs-compliant, being compliant with 11 SDGs (SDG-2, SDG-3, SDG-6, SDG-7, SDG-9, SDG-11, SDG-13, SDG-14, SDG-15).
So, back to those studies that the United Nations University recommends…
A multi-perspective knowledge-driven approach for analysis of the demand side of the Open Government Data portal, which proposes a multi-perspective approach where an OGD portal is analyzed from (1) citizens’ perspective, (2) users’ perspective, (3) experts’ perspective, and (4) state of the art. By considering these perspectives, we can define how to improve the portal in question by focusing on its demand side. In view of the complexity of the analysis, we look for ways to simplify it by reusing data and knowledge on the subject, thereby proposing a knowledge-driven analysis that supports the idea under OGD – their reuse. Latvian open data portal is used as an example demonstrating how this analysis should be carried out, validating the proposed approach at the same time. We are aiming to find (1) the level of the citizens’ awareness of the portal existence and its quality by means of the simple survey, (2) the key challenges that may negatively affect users’ experience identified in the course of the usability analysis carried out by both users and experts, (3) combine these results with those already known from the external sources. These data serve as an input, while the output is the assessment of the current situation allowing defining corrective actions. Since the debates on the Latvian OGD portal serving as the use-case appear more frequently, this study also brings significant benefit at national level.
Transparency of open data ecosystems in smart cities: Definition and assessment of the maturity of transparency in 22 smart cities, which focuses on the issue of the transparency maturity of open data ecosystems seen as the key for the development and maintenance of sustainable, citizen-centered, and socially resilient smart cities. This study inspects smart cities’ data portals and assesses their compliance with transparency requirements for open (government) data. The expert assessment of 34 portals representing 22 smart cities, with 36 features, allowed us to rank them and determine their level of transparency maturity according to four predefined levels of maturity – developing, defined, managed, and integrated. In addition, recommendations for identifying and improving the current maturity level and specific features have been provided. An open data ecosystem in the smart city context has been conceptualized, and its key components were determined. Our definition considers the components of the data-centric and data-driven infrastructure using the systems theory approach. We have defined five predominant types of current open data ecosystems based on prevailing data infrastructure components. The results of this study should contribute to the improvement of current data ecosystems and build sustainable, transparent, citizen-centered, and socially resilient open data-driven smart cities.
Smarter open government data for society 5.0: Are your open data smart enough? in which, considering the fact that the open (government) data initiative as well as users’ intent for open (government) data are changing continuously and today, in line with IoT and smart city trends, real-time data and sensor-generated data have higher interest for users that are considered to be one of the crucial drivers for the sustainable economy, and might have an impact on ICT innovation and become a creativity bridge in developing a new ecosystem in Industry 4.0 and Society 5.0, the paper examines 51 OGD portals on the presence of the relevant data and their suitability for further reuse, by analyzing their machine-readability, currency or frequency of updates, the ability to submit request/comment/complaint/suggestion and their visibility to other users, and the ability to assess the value of these data assessed by others, i.e., rating, reuse, comments, etc., which is usually considered to be a very time-consuming and complex task, and therefore rarely conducted. The analysis leads to the conclusion that although many OGD portals and data publishers are working hard to make open data a useful tool moving towards Industry 4.0 and Society 5.0, many portals do not even respect the principles of open data, such as machine-readability. Moreover, according to the lists of most competitive countries by topic, there are no leaders who provide their users with excellent data and service, therefore there is room for improvements for all portals. The paper shows that open data, particularly those published and updated in time, are provided in machine-readable format and support to their users, attract audience interest and are used to develop solutions that benefit the entire society (the case in France, Spain, Cyprus, the Netherlands, Taiwan, Austria, Switzerland, etc.). Thus, the publication of open data should be done not only because it is a modern trend, but also because it incentivizes scientists, researchers and enthusiasts to reuse the data by transforming it into knowledge and value, providing solutions, improving the world, and moving towards Society 5.0 or the super smart society.
Definition and evaluation of data quality: User-oriented data object-driven approach to data quality assessment proposes a data object-driven approach to data quality evaluation. This user-oriented solution is based on 3 main components: data object, data quality specification and the process of data quality measuring. These components are defined by 3 graphical DSLs, that are easy enough even for non-IT experts. The approach ensures data quality analysis depending on the use-case. Developed approach allows analysing quality of “third-party” data. The proposed solution is applied to open data sets. The result of approbation of the proposed approach demonstrated that open data have numerous data quality issues. There are also underlined common data quality problems detected not only in Latvian open data but also in open data of 3 European countries – Estonia, Norway, the United Kingdom. I.e., none of the very simple or intuitive and even obvious use cases in which the values of the primary parameters were analysed were satisfied by any Company Register. However, the Estonian and Norwegian Registers can be used to identify any company by its name and registration number, since only they have passed quality checks of the relevant fields.
Open Data Hackathon as a Tool for Increased Engagement of Generation Z: To Hack or Not to Hack? examines the role of open data hackathons, known as a form of civic innovation in which participants representing citizens can point out existing problems or social needs and propose a solution, in OGD initiative. Given the high social, technical, and economic potential of open government data (OGD), the concept of open data hackathons is becoming popular around the world. This concept has become popular in Latvia with the annual hackathons organised for a specific cluster of citizens – Generation Z. Contrary to the general opinion, the organizer suggests that the main goal of open data hackathons to raise an awareness of OGD has been achieved, and there has been a debate about the need to continue them. This study presents the latest findings on the role of open data hackathons and the benefits that they can bring to both the society, participants, and government. First, a systematic literature review is carried out to establish a knowledge base. Then, empirical research of 4 case studies of open data hackathons for Generation Z participants held between 2018 and 2021 in Latvia is conducted to understand which ideas dominated and what were the main results of these events for the OGD initiative. It demonstrates that, despite the widespread belief that young people are indifferent to current societal and natural problems, the ideas developed correspond to current situation and are aimed at solving them, revealing aspects for improvement in both the provision of data, infrastructure, culture, and government- related areas.
More to come, and let’s keep track of updates in this repository! Do not also to check other works in both the repository, as well as more work of mine you can find here.
“Meet the publishers” or “Meet me with the Data & Policy” (Cambridge University Press) at CUDAN2023
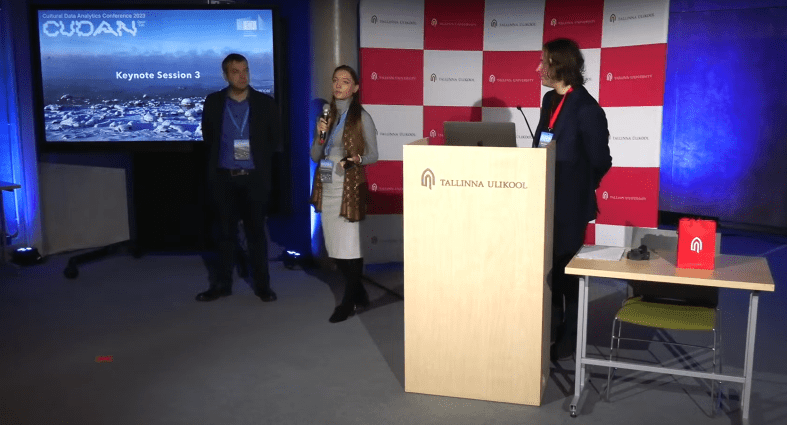
Cultural Data Analytics Conference 2023 (CUDAN 2023) took place this week at Tallinn University, where I was kindly invited by the organizers to take part in the Meet The Publishers session representing Data & Policy journal (Cambridge University Press), where I serve as editor for “Focus on Digital & Data-Driven Transformations in Governance” area.
Together with colleague – Innar Liiv, who kindly joined me in promoting our journal, Data & Policy was represented by researchers representing two leading universities in Estonia – University of Tartu and TalTech – Tallinn University of Technology. The conference was hosted by another large Estonian university – Tallinn University, which did a great job since, although I am not related to cultural data analytics, I enjoyed the sessions, keynotes – Mauro Martino from IBM Research, Anu Masso from TalTech – Tallinn University of Technology, Lev Manovich from The City University of New York, and AI Art exhibition as part of a social event. Thank you Maximilian Schich for this event and invitation!





Referring back to the “Meet the Data & Policy“, and delivering the main message of this post – I invite you all to do the same and consider this relatively new but increasingly popular journal with a very good reputation.
Do not forget also the Special Issues we have, one of which is co-edited by me (together with Jérôme Chenal, EPFL (École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne), Cédric Stéphane Teakouabou Koumetio, UM6P – Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, El Arbi Abdellaoui Alaoui) and is devoted to Emerging Data- and Policy-driven Approaches for African Cities Challenges, with a submission deadline of January 8, 2024. Just to remind, this Special Issue aims to expand the reach and scope of urban data research, innovation and entrepreneurship activities and policies to address urban challenges in Africa through the digitisation of cities. It will compile recent expert work on the topic to advance and promote scientific advance / excellence, promote the digital transition and its benefits for creating, collecting, storing and using urban data to achieve sustainable development goals (SDG) in African cities.
You can read more about the call in my previous post.
CFP for The IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication, Networking and Services (ICCNS2023)
On behalf of the organizers (Technical Program Chair, Steering Committee, and finally publicity chair) of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication, Networking and Services (ICCNS2023), I am inviting everyone, who is conducting research in this area, to consider submitting the paper to it.
Call for Papers:
New advancements in wireless communication systems such as Fifth-Generation (5G), Beyond Fifth-Generation (B5G), and Sixth-Generation (6G) networks will allow for new and unprecedented services to be made available for users with nearly unlimited capacity. These services will be the core driver for future digital transformation of our cities and communities. This will be accompanied by a ubiquitous deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure and supported by computing capacity that will be available at the edge of the network and in the cloud. This computing infrastructure will handle the processing of data generated by users and services. Such a complex and diverse system will require the applications running on the computing/networking infrastructure to be Intelligent, efficient and sustainable. Additionally, the infrastructure will require smart control and automation systems to integrate and manage its different components. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its applications will play a significant role in the design, deployment, automation, and management of future services. This will include applications that will be running on the edge and on cloud servers, networking applications to handle the flow of data between the users and the computing system, and intelligent automation and management software operating on the system. The International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Networking, and Services is aiming to provide an opportunity to present state of the art research in the intersections of Computing, Networking, and Services that are supported by Artificial Intelligence.
Submission Link: https://easychair.org/conferences/?conf=iccns2023
Researchers from both the industry and academia are encouraged to submit their original research contributions in all major areas, which include, but are not limited to the following main tracks:
💡Track 1: Artificial Intelligence Fundamentals
- Artificial Intelligent Systems
- Artificial Intelligent Theory
- Artificial Intelligent applications in Computers and Communications
- Artificial Intelligent and Robotics Technologies
- Artificial Intelligent and cloud computing
- Artificial Intelligent for Economic paradigms and game theory
- Machine and Deep Learning of Knowledge
- Artificial Intelligent based Distributed Knowledge and Processing
- Artificial Intelligent for Human-Robot Interactions
💡Track 2: Intelligent Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems
- Intelligent IoT Applications and Services
- Intelligent security for the Internet of Things and cyber-physical systems
- Intelligent Internet of Things architectures and protocols
- Intelligent Cyber Physical Systems (CPS)
- Blockchain-based application in Intelligent Manufacturing: Industrial Internet of Things,
- Blockchain and Secure Critical Infrastructure with Industry 4.0
- Intelligent manufacture and management
- Consensus and mining algorithms suited for resource-limited IoTs
- Blockchain-based Controlled mobility and QoS
- Blockchain-based energy optimization techniques in WSN
- Blockchain-based Software defined networks
💡Track 3: Edge Intelligence and Federated Learning
- Distributed and federated machine learning in edge computing
- Theory and Applications of Edge Intelligence
- Middleware and runtime systems for Edge Intelligence
- Programming models compliant with Edge Intelligence
- Scheduling and resource management for Edge Intelligence
- Data allocation and application placement strategies for Edge Intelligence
- Osmotic computing with edge continuum, Microservices and MicroData architectures
- ML/AI models and algorithms for load balancing
- Theory and Applications of federated learning
- Federated learning and privacy-preserving large-scale data analytics
- MLOps and ML pipelines at edge computing
- Transfer learning, interactive learning, and Reinforcement Learning for edge computing
- Modeling and simulation of EI and edge-to-cloud environments
- Security, privacy, trust, and provenance issues in edge computing
- Distributed consensus and blockchains at edge architecture
- Blockchain networking for Edge Computing Architecture
- Blockchain technology for Edge Computing Security
- Blockchain-based access controls for Edge-to-cloud continuum
- Blockchain-enabled solutions for Cloud and Edge/Fog IoT systems
- Forensic Data Analytics compliant with Edge Intelligence
💡Track 4: Intelligent Networking in Beyond 5G (B5G) and 6G Wireless Communication
- Intelligent Networking in Beyond 5G/6G Network Architectures
- large-scale Internet of Things in B5G/6G
- Vehicular networks in B5G/6G
- Blockchain with lightweight computation
- Service and applications for vehicular clouds in B5G/6G
- Future internet architectures for B5G/6G
- Intelligent networking services
- Emerging networks in B5G/6G
- Byzantine-tolerant FL
- Churn-tolerant FL
- FL for NGN and 6G
- B5G/6G based IoT healthcare systems
💡Track 5: Intelligent Big Data Management and Processing
- Intelligent Data Fusion
- Intelligent Analytics and Data mining
- Intelligent Distributed data management
- Distributed transaction for blockchain
- Intelligent Data Science and Data Engineering
- Protocols for management and processing of data
💡Track 6: Intelligent Security and Privacy
- Authentication and authorization
- Applications of blockchain technologies in digital forensic
- Privacy technologies
- Blockchain-based threat intelligence and threat analytics techniques
- Blockchain-based open-source tools
- Forensics readiness of blockchain technologies
- Blockchain Attacks on Existing Systems
- Blockchain Consensus Algorithms
- Blockchain-based Intrusion Detection/Prevention
- Security and Privacy in Blockchain and Critical Infrastructure
- Attacks on Blockchain and Critical Infrastructure
- Blockchain and Secure Critical Infrastructure with Smart Grid
💡Track 7: Blockchain Research & Applications for Intelligent Networks and Services
- State-of-the-art of the Blockchain technology and cybersecurity
- Blockchain-based security solutions of smart cities infrastructures
- Blockchain in connected and autonomous vehicles (CAV) and ITS)
- Blockchain Technologies and Methodologies
- Recent development and emerging trends Blockchain
- New models, practical solutions and technological advances related to Blockchain
- Theory of Blockchain in Cybersecurity
- Applications of blockchain technologies in computer & hardware security
- Implementation challenges facing blockchain technologies
- Blockchain in social networking
- Performance metric design, modeling and evaluation of blockchain systems
- Network and computing optimization in blockchains
- Experimental prototyping and testbeds for blockchains
- Blockchain networking for Edge Computing Architecture
- Blockchain technology for Edge Computing Security
- Blockchain-based access controls for Edge-to-cloud continuum
- Blockchain-enabled solutions for Cloud and Edge/Fog IoT systems
- Forensic Data Analytics compliant with Edge Intelligence
Two workshops are scheduled to take place as part of ICCNS that you cannot miss, namely:
- The Third International Workshop on Deep and Transfer Learning (DTL2023) that aims to bridge the gap between theories and practices by providing the researchers and practitioners the opportunity to share ideas and discuss and criticize current theories and results. We invite the submission of original papers on all topics related to deep learning, deep reinforcement learning, and transfer and multi-task learning;
- The International Workshop on Computing for Pandemics (COMPandemics2023)
🗓️🗓️🗓️ IMPORTANT DATES
- Full paper submission: April 21st, 2023 (Firm and Final)
- Full paper acceptance notification: May 6th, 2023
- Full paper camera-ready submission: May 20th, 2023
For any inquiries, please contact: intelligenttechorg@gmail.com.
Submit the paper and meet our team in Valencia in June, 2023!
With best wishes,
ICCNS2023 organizers
The International Open Data Day and my role of Keynote Speaker for the 5th International Conference on Advanced Research Methods and Analytics (CARMA 2023) 🎤🎤🎤
This post is dedicated to two very pleasant events for me, namely the international Open Data Day 🎉🍾🥂, and the announcement of the keynote talk that I was kindly invited to deliver at the 5th International Conference on Advanced Research Methods and Analytics (CARMA) organized and sponsored by Universidad de Sevilla, Cátedra Metropol Parasol, Cátedra Digitalización Empresarial, IBM, Universitat Politècnica de València, Joint Research Center – European Commission and 🥁 🥁 🥁 Coca-Cola – what a delicious conference!🍸🍸🍸

CARMA is a forum for researchers and practitioners to exchange ideas and advances on how emerging research methods and sources are applied to different fields of social sciences as well as to discuss current and future challenges with main focus on the topics such as Internet and Big Data sources in economics and social sciences including Social media and public opinion mining, Web scraping, Google Trends and Search Engine data, Geospatial and mobile phone data, Open data and public data, Big Data methods in economics and social sciences such as Sentiment analysis, Internet econometrics, AI and Machine learning applications, Statistical learning, Information quality and assessment, Crowdsourcing, Natural Language processing, Explainability and interpretability, the applications of the above including but not limited to Politics and social media, Sustainability and development, Finance applications, Official statistics, Forecasting and nowcasting, Bibliometrics and sciencetometrics, Social and consumer behaviour, mobility patterns, eWOM and social media marketing, Labor market, Business analytics with social media, Advances in travel, tourism and leisure, Digital management, Marketing Intelligence analytics, Data governance, and Digital transition and global society, which, in turn, expects contributions in relation to Privacy and legal aspects, Electronic Government, Data Economy, Smart Cities, Industry adoption.
And as almost each and every conference, CARMA expects to have keynotes, which are two – Patrick Mikalef, who will talk about Responsible AI and Big Data Analytics, and me, whose keynote talk will be devoted to the topics I studied in recent years titled “Public data ecosystems in and for smart cities: how to make open / Big / smart / geo data ecosystems value-adding for SDG-compliant Smart Living and Society 5.0?” Sounds interesting? (I hope so) Stay tuned to know more! And return back, since I plan to reflect on the content of both talks and the conference in general.
The CARMA 2023 conference will be held on 28 June – 30 June 2023 in the University of Seville.