Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping how societies govern, deliberate, and make collective decisions. Over the past year, our Democracy & AI workshop series—held across IJCAI, PRICAI, and ICA—has become a global forum for examining both the promise and the perils of AI in democratic contexts. From Montréal to Wellington to Wuhan, our community continues to grow, connecting researchers across AI, political science, HCI, law, design, ethics, and public administration.
DemocrAI at IJCAI 2025: AI at the Service of Society
As part of the IJCAI International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence in Montréal, themed “AI at the service of society,” we (Jawad Haqbeen, Takayuki Ito, Rafik Hadfi, and myself) convened the 6th International Workshop on Democracy & AI (DemocrAI25).
Although I could not attend in person, I am deeply grateful to my co-organizers for leading the workshop and for representing our team—as well as for the chance to meet Yoshua Bengio, one of the pioneers of modern deep learning and the one who recently became the very first researcher who while still being active in research achieved the milestone of 1 million citations!
The workshop opened with two outstanding keynote talks:
- Mary Lou Maher (UNC Charlotte) — “The Imperative for AI Literacy”
- Michael Inzlicht (University of Toronto) — “In Praise of Empathic AI”
Across 13 diverse presentations, contributors explored: AI’s impact on trust, civic engagement, and deliberation, risks and governance of LLMs in judicial settings and policymaking, collective intelligence and value aggregation for democratic processes, AI applications in education, law, and policy design, governance, fairness, inclusion, and global research equity.
We were delighted to recognize several exceptional contributions:
- Best Paper Award — “LLMs in Court: Risks and Governance of LLMs in Judicial Decision-Making” (Djalel Bouneffouf & Sara Migliorini)
- Best Student Paper Award — “Finding Our Moral Values: Guidelines for Value System Aggregation” (Víctor Abia Alonso, Marc Serramia & Eduardo Alonso Sánchez)
- Best Extended Abstract Award — “Group Discussions Are More Positive with AI Facilitation” (Sofia Sahab, Jawad Haqbeen & Takayuki Ito)
- Best Presentation Award — “Democracy as a Scaled Collective Intelligence Process” (Marc-Antoine Parent)
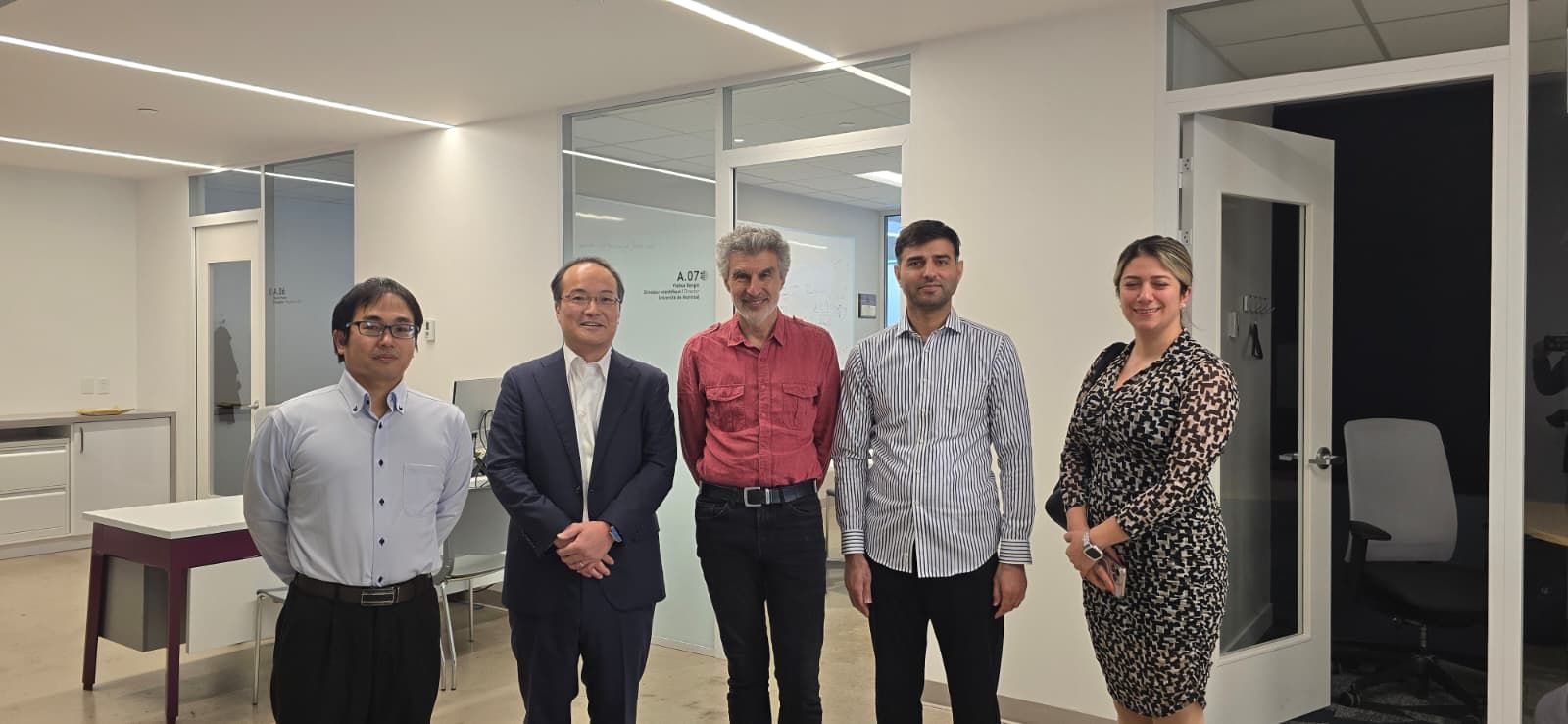



A key message echoed throughout the day: AI can enhance social cohesion, participation, and equity—but only through responsible design and robust governance frameworks.
DemocrAI at PRICAI 2025: Participation, Values, and Governance
Following IJCAI, I joined the organizing committee for the 7th Democracy & AI Workshop at PRICAI 2025, held in Wellington, New Zealand. Two years ago, I had the privilege of giving a keynote at PRICAI DemocrAI on symbiotic relationship of Artificial Intelligence, Data Intelligence, and Collaborative Intelligence for Innovative Decision-Making and Problem Solving. This year, I am excited to help shape the conversation from the organizing side.
The workshop explored the expanding role of AI in democratic life, including AI-assisted policy design and decision-making, AI in governance, elections, and public administration, citizen participation and deliberative democracy tools, behavioral impacts of AI on trust, engagement, and polarization, transparency, accountability, and legitimacy of algorithmic decisions, ethics, socio-technical risks, and AI’s impact on societal wellbeing, and reimagining democracy in the LLM era.




Special Track at ICA 2025: AI in e-Government & Public Administration
Our workshop series expands further with a dedicated Special Track on AI in e-Government & Public Administration at the IEEE International Conference on Agentic AI (ICA 2025), held in Wuhan, China.
Co-organized with Jawad Haqbeen, Takayuki Ito, and Torben Juul Andersen, this track examines how AI-driven tools are transforming public governance—from policy co-creation and civic engagement to service delivery and institutional decision-making.
Topics include:
- AI for participatory and deliberative governance
- AI’s impact on societal wellbeing
- AI in public service delivery and policy design
- Ethics and risk governance in public-sector AI
- Case studies and experiments with deployed systems
- Transparency, accountability, and responsible administration

Across IJCAI, PRICAI, and ICA, one theme is clear: AI’s role in democracy is neither predetermined nor neutral. It can support inclusion, transparency, and collective intelligence—or undermine trust, equity, and participation. The outcome depends on the choices we make now: the values we embed, the governance we build, and the communities we bring together.
Our Democracy & AI workshop series exists to advance this work—uniting technologists, policymakers, social scientists, designers, and ethicists in a shared mission: to ensure AI serves democracy, rather than the other way around.
Huge thanks to all speakers, awardees, participants, and co-organizers.
Onward to DemocrAI at PRICAI and ICA 2025!