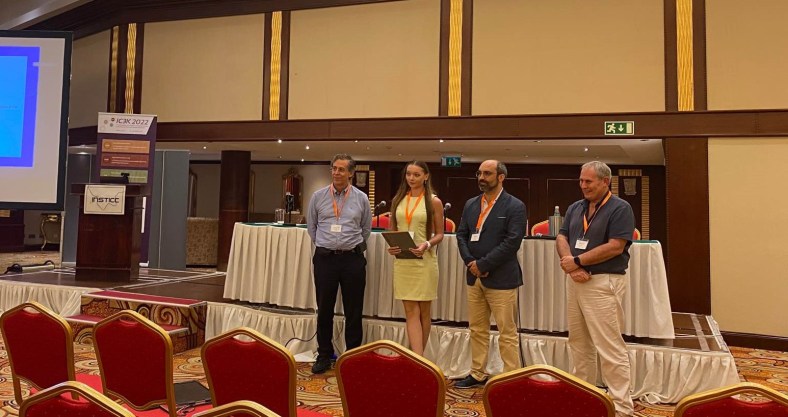
In this post I would like to briefly elaborate on a truly insightful 14th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K), where I was honored to participate as a speaker, presenting our paper “Putting FAIR principles in the context of research information: FAIRness for CRIS and CRIS for FAIRness” (authors: Otmane Azeroual, Joachim Schopfel and Janne Polonen, and Anastasija Nikiforova), and as a chair of two absolutely amazing sessions, where live and fruitful discussions took place, which is a real indicator of the success of such! And spoiler, our paper was recognized as the Best Paper! (i.e., best paper award goes to… :))
IC3K consists of three subconferences, namely 14th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval (KDIR), 14th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development (KEOD), and 14th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems (KMIS), where the latter is the one, to which my paper has been accepted, and also won the Best Paper Award – I know, this is a repetition, but I am glad to receive it, same as the euroCRIS community is proud for us – read more here…!
Briefly about our study, with which we mostly wanted to urge a call for action in the area of CRIS and their FAIRness. Of course, this is all about the digitization, which take place in various domain, including but not limited to the research domain, where it refers to the increasing integration and analysis of research information as part of the research data management process. However, it is not clear whether this research information is actually used and, more importantly, whether this information and data are of sufficient quality, and value and knowledge could be extracted from them. It is considered that FAIR principles (Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, Reusability) represent a promising asset to achieve this. Since their publication (by one of the colleagues I work together in European Open Science Cloud), they have rapidly proliferated and have become part of both national and international research funding programs. A special feature of the FAIR principles is the emphasis on the legibility, readability, and understandability of data. At the same time, they pose a prerequisite for data and their reliability, trustworthiness, and quality. In this sense, the importance of applying FAIR principles to research information and respective systems such as Current Research Information Systems (CRIS, also known as RIS, RIMS), which is an underrepresented subject for research, is the subject of our study. What should be kept in mind is that the research information is not just research data, and research information management systems such as CRIS are not just repositories for research data. They are much more complex, alive, dynamic, interactive and multi-stakeholder objects. However, in the real-world they are not directly subject to the FAIR research data management guiding principles. Thus, supporting the call for the need for a ”one-stop-shop and register-once use-many approach”, we argue that CRIS is a key component of the research infrastructure landscape / ecosystem, directly targeted and enabled by operational application and the promotion of FAIR principles. We hypothesize that the improvement of FAIRness is a bidirectional process, where CRIS promotes FAIRness of data and infrastructures, and FAIR principles push further improvements to the underlying CRIS. All in all, three propositions on which we elaborate in our paper and invite everyone representing this domain to think of, are:
1. research information management systems (CRIS) are helpful to assess the FAIRness of research data and data repositories;
2. research information management systems (CRIS) contribute to the FAIRness of other research infrastructure;
3. research information management systems (CRIS) can be improved through the application of the FAIR principles.
Here, we have raised a discussion on this topic showing that the improvement of FAIRness is a dual or bidirectional process, where CRIS promotes and contributes to the FAIRness of data and infrastructures, and FAIR principles push for further improvement in the underlying CRIS data model and format, positively affecting the sustainability of these systems and underlying artifacts. CRIS are beneficial for FAIR, and FAIR is beneficial for CRIS. Nevertheless, as pointed out by (Tatum and Brown, 2018), the impact of CRIS on FAIRness is mainly focused on the (1) findability (“F” in FAIR) through the use of persistent identifiers and (2) interoperability (“I” in FAIR) through standard metadata, while the impact on the other two principles, namely accessibility and reusability (“A” and “R” in FAIR) seems to be more indirect, related to and conditioned by metadata on licensing and access. Paraphrasing the statement that “FAIRness is necessary, but not sufficient for ‘open’” (Tatum and Brown, 2018), our conclusion is that “CRIS are necessary but not sufficient for FAIRness”.
This study differs significantly from what I typically talk about, but it was to contribute to it, thereby sharing the experience I gain in European Open Science Cloud (EOSC), and respective Task Force I am involved in – “FAIR metrics and data quality”. It also allowed me to provide some insights on what we are dealing with within this domain and how our activities contribute to the currently limited body of knowledge on this topic.
A bit about the sessions I chaired and topics raised within them, which were very diverse but equally relevant and interesting. I was kindly invited to chair two sessions, namely “Big Data and Analytics” and “Knowledge management Strategies and Implementations”, where the papers on the following topics were presented:
- Decision Support for Production Control based on Machine Learning by Simulation-generated Data (Konstantin Muehlbauer, Lukas Rissmann, Sebastian Meissner, Landshut University of Applied Sciences, Germany);
- Exploring the Test Driven Development of a Fraud Detection Application using the Google Cloud Platform (Daniel Staegemann, Matthias Volk, Maneendra Perera, Klaus Turowski, Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Germany) – this paper was also recognized as the best student paper;
- Decision Making with Clustered Majority Judgment (Emanuele D’ajello , Davide Formica, Elio Masciari, Gaia Mattia, Arianna Anniciello, Cristina Moscariello, Stefano Quintarelli, Davide Zaccarella, University of Napoli Federico II, Copernicani, Milano, Italy.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Technology Integration in the Training Environment Leads to Behaviour Change (Amy Rosellini, University of North Texas, USA)
- Innovation in Boutique Hotels in Valletta, Malta: A Multi-level Investigation (Kristina, University of Malta, Malta)
And, of course, as is the case for each and every conference, the keynotes are panelists are those, who gather the highest number of attendees, which is obvious, considering the topic they elaborate on, as well as the topics they raise and discuss. IC3K is not an exception, and the conference started with a very insightful discussion on Current Data Security Regulations and the discussion on whether they Serve or rather Restrict the Application of the Tools and Techniques of AI. Each of three speakers, namely Catholijn Jonker, Bart Verheijen, and Giancarlo Guizzardi, presented their views considering the domain they represent. As a result, both were very different, but at the same time leading you to “I cannot agree more” feeling!
One of panelists – Catholijn Jonker (TU Delft) delivered then an absolutely exceptional keynote speech on Self-Reflective Hybrid Intelligence: Combining Human with Artificial Intelligence and Logic. Enjoyed not only the content, but also the style, where the propositions are critically elaborated on, pointing out that they are not indented to serve as a silver bullet, and the scope, as well as side-effects should be determined and considered. Truly insightful and, I would say, inspiring talk.
All in all, thank you, organizers – INSTICC (Institute for Systems and Technologies of Information, Control and Communication), for bringing us together!